Lightning Learning: Otitis Media (Diagnosis & Management)
STOP!
80% of children experience at least one episode of Acute Otitis Media (AOM) before 2 years. AOM occurs in <1% of adults.
Risk Factors
Children with anatomical anomalies (e.g. cleft palate) or immunological deficiencies.
Environmental: childcare attendance, exposure to older siblings, exposure to tobacco smoke, bottle feeding in a supine position, dummy use.
Male
Family history of AOM
Certain ethnic groups (Native Americans & Native Alaskans)
LOOK
Key factors of history will vary with age. Discussed by CKS NICE.
Examination (not exhaustive)
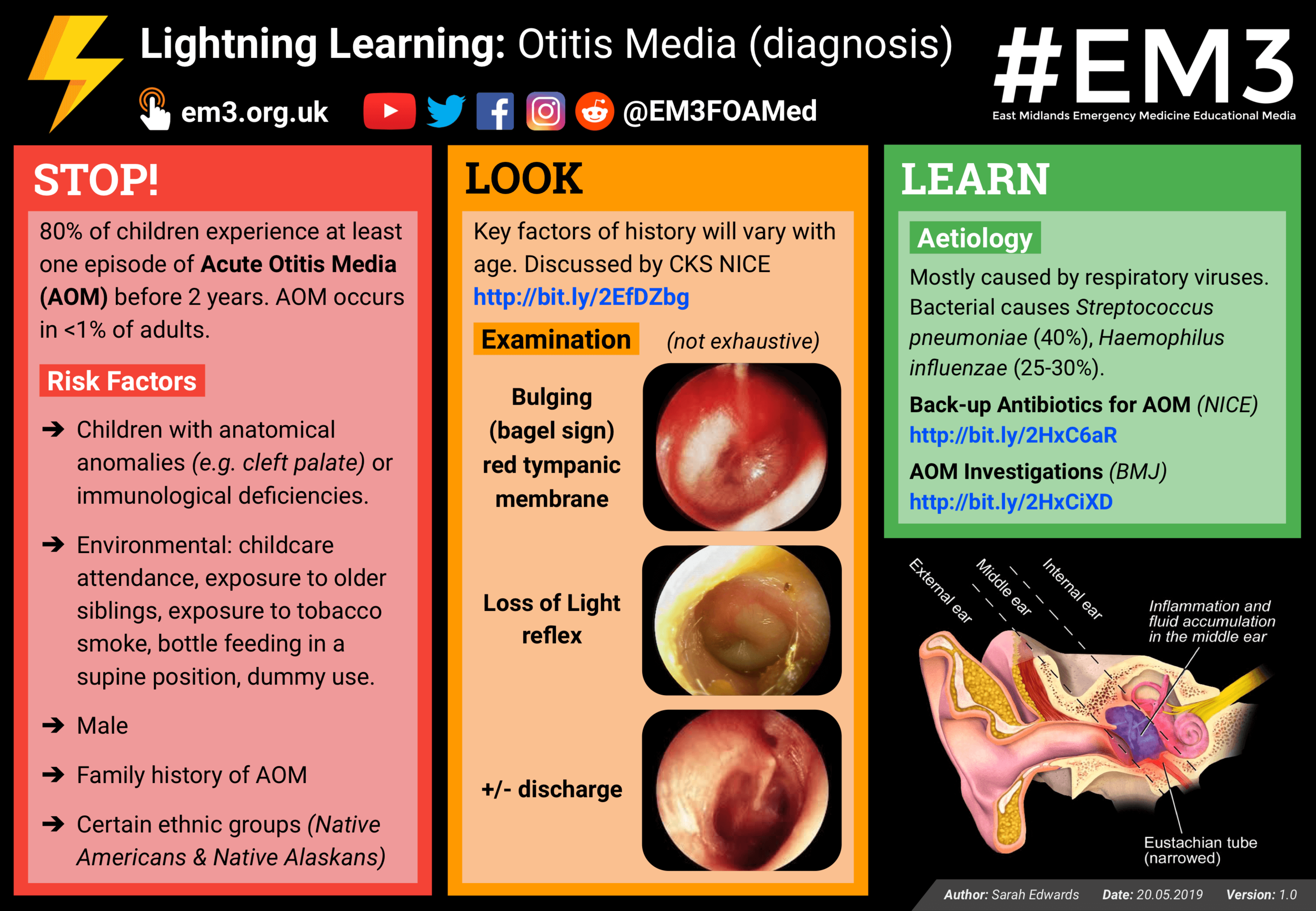
Bulging (bagel sign) red tympanic membrane
Loss of Light reflex
+/- discharge
LEARN
Aetiology? Mostly caused by respiratory viruses. Bacterial causes Streptococcus pneumoniae (40%), Haemophilus influenzae (25-30%).
- Back-up Antibiotics for AOM (NICE Guidance)
- AOM Investigations (BMJ Best Practice)
STOP!
80% of children experience at least one episode of Acute Otitis Media (AOM) before 2 years.
“How should I manage people at their initial presentation?”
Admit if…
Person with severe infection
Person with suspected complications of AOM
Child <3 months with temp >38°C
Consider admission if…
Child <3 months old
Child 3-6 months with temp >39°C
All people with AOM
Course of AOM 3-7 days
Advise regular analgesia such as paracetamol/ibuprofen
LOOK
Who benefits from immediate antibiotics?
Those with presence of otorrhoea
Anyone aged less than 2 years with bilateral infection
The systemically unwell
Those with high risk of complications.
What about delayed prescriptions?
Expert consensus suggests that AOM could be viral or bacterial and distinguishing can be difficult. Therefore, backup or no antibiotic prescription could be considered in most children with AOM.
Between 2-5 years you need to treat 16,000 children for AOM to prevent 1 case of mastoiditis.
LEARN
Treatment? Amoxicillin or Erythromycin/Clarithromycin
- Back-up Antibiotics for AOM (NICE Guidance)
- AOM Investigations (BMJ Best Practice)